OOP’s Concept in Java : OOP’s concept stands for Object Oriented Programming concept in java and it is design to make effective, easy to understand and to save developers efforts in terms of coding and time. There are four major pillars of object oriented programming such as Inheritance, Polymorphism, Abstraction and Encapsulation.
Inheritance in Java
Inheritance is nothing but a mechanism where one class can acquire the properties of another class, all you need to do is to create Parent-Child relation between those two classes.
Is-A Relationship :-
1) Inheritance is also called as “Is-A Relationship”.
2) Main advantage of inheritance is Re-usability of code.
3) This concept can be achieved by using “extends” keyword.
4) We can avoid duplication of code by using inheritance.
5) We can acquire all the properties of parent class into child class by using inheritance.
Example :-
a) MS Office comes with different versions such as MS Office 2000, 2007, etc. It doesn’t means that developer always code newly, they use same existing code with additional features only.
b) We came across different versions of mobile phones.
When to Use Is-A relationship :-
Whenever we required all the properties /data of parent class then you must go for “Is-A Relationship”.
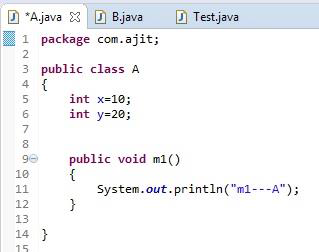
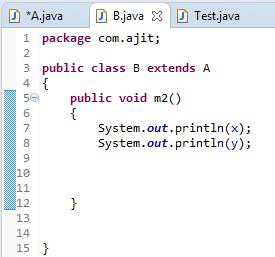
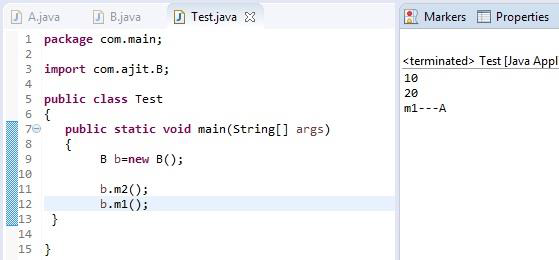
Please refer below piece of code for Is-A Relationship :-
Has-A Relationship :-
1) It is also called as “Composition”.
2) Composition:- Strong association between container and contained class.
Aggregation:- Weak association between container and contained class.
3) Has-A relationship doesn’t have any keyword to implement Has-A relationship such as “extends”.
Example:-
a) House Has-A Kitchen but Kitchen doesn’t has House (House contained Kitchen but Kitchen can’t contained House).
b) Car Has-A Engine but Engine doesn’t has Car (Car contained Engine but Engine doesn’t contained Car).


When to Use Has-A relationship :-
Whenever we required particular data of parent class into child class then you must go for “Has-A Relationship” instead of “Is-A Relationship”.
Please refer below piece of code for Has-A Relationship :-



In the above example, Class B extends Class A that means that class A is a parent/super class and class B is child/sub class.
So, we can write such as:-
A a=new A();
A a=new B();
B b=new B();
But we can not write such as:-
B b=new A();
Because, Parent reference can hold the child object but child reference can not hold the parent object.

Polymorphism in Java
Polymorphism it means “One name, Many forms”.
The main purpose of polymorphism is to made readability simple and understanding easy.
There are two types of Polymorphism as follows :-
1) Compile time Polymorphism (Overloading / Static Binding)
2) Run time Polymorphism (Overriding/ Dynamic Binding)
Compile time Polymorphism (Overloading / Static Binding) :-
1) It is called as Compile time Polymorphism, because all the decisions are taken by compiler only.
2) Whenever we required to write same name multiple method in a single class with different method parameter then it is called as “Method Overloading”.
3) Whenever we required to write same name multiple constructor in a single class with different constructor parameter then it is called as “Constructor Overloading”.
4) Method overloading happens in between same class or in between parent-child class.
5) Constructor overloading always happen only in same class.
6) We can overload Static, Private, Final method.
7) Syntax rules for method overloading:-
a) Method name must be same.
b) Method parameter must be different.
c) Return type of method doesn’t matter.
d) Access modifiers doesn’t matter.

Narrowing Concept :-
1) Suppose we have two methods with same name but different parameter and we passed parameter at the time of method calling, if that parameter is valid for both the method then Child method will get executed first as shown in above example.
2) Suppose we have Three methods with same name but different parameter and we passed parameter at the time of method calling, if that parameter is valid for all three methods and if out of that three methods there is Child-Child relation along with parent-child relation then Program will show ambiguity error as shown in below figure.
If we want to called those all three methods then we need to type cast the parameter as shown in below figure (Commented code).

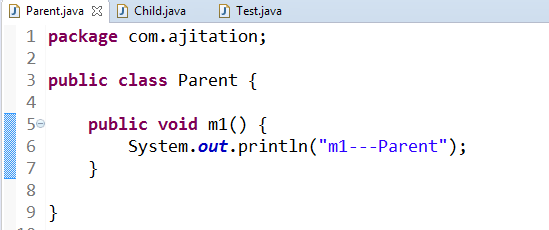
Runtime Polymorphism (Overriding / Dynamic Binding) :-
1) Whenever existing functionality present with additional functionality with same method signature then it is called as “Method Overrding”.
2) Method overriding happens in between parent-child class only.
3) We can override method only, We can not override Constructor.
4) We can not override Static, Private, Final method.
5) Syntax rules for method overloading:-
a) Method name must be same.
b) Method parameter must be same.
c) If return type is void or primitive then it must be same.
d) If return type is user define data member then it must be same or sub-class.



e) Access modifiers must be same or greater (Strong) , it must not be weaker. If child class method access modifier is weaker than parent class method access modifier then it will give error to “Change visibility“
( Public > Protected > Default > Private )

We can not Override Static, Private, Final method because,
1) Private :- private method scope will always remain up to that class only.
2) Final :- If method is final then it can not be changed.
3) Static :- If we have a static methods in super class and subclass with same signature then we don’t say that as overriding, we call that as “Method Hiding”.
We can override method only, We can not override Constructor, because constructor name must be same as Class name.
Abstraction in Java
Abstraction it means that hiding internal implementation and just highlighting the purpose only.
Best example of abstraction that we all commonly use is println() method.
In java we can achieve abstraction by using Interface and Abstract class.
There are several places where we use abstraction such as:
- Third party communication (ex: Railway / Bus Ticket Booking, Bank Transaction)
- API Development
- Development of Project structure and layout
Interface :-
1) Interface is collection of abstract method and variables, we can say that Interface is pure or 100% abstract class. (this is valid for up to java 1.7 version only, because in Java 1.8 we can have implemented methods as well in an interface)
2) Interface acts like communicator between two objects.
3) Interface provides rules and guidelines for project development which has to implement in our project.
Just like RBI, RBI provides rules and guidelines which has to get implemented by all other banks. (Interface gets implemented by classes)
4) We can not create object of an interface. Example : I i=new I();
5) We have to initialize values of variable as it is public final, whereas no need to initialize in class.
6) Method will be end with semi-colon and it is automatically public abstract.
7) Interface supports multiple inheritance,
Example :
public interface I3 extends I1,I2
{ //abstract methods
}

If one interface extends multiple interfaces and that multiple interface method name and parameter is same but return type is different then interface will not allow to extends multiple interface.

Marker Interface :-
Marker interface is an interface with blank body, it means that it does not have any data member or methods.
Marker interface is use for decision making purpose, if you implement marker interface in class then that class will get marked as permitted class to get executed.
( It is use for sorting purpose )

If we doesn’t implement marker interface then we will get output as shown in below figure :-

Abstract class :-
Abstract class is those class which consist of implemented (Concrete) as well as non-implemented class (Abstract).
If any one method of a class is abstract then that class must be abstract or else you need to remove “abstract” modifier from method signature as shown in below snippet:


We can not create an object of Abstract class as follows :

Even though class does not have any abstract method we can make class as abstract to restrict the class, so that no one can create object of that class.

How we can call abstract class implemented method?
By using sub class (Child class).
Is there any constructor inside of abstract class?
Yes, by default it is present and access modifier of constructor will be public.
If we want to create child class of an abstract class which have both type of method (abstract as well as implemented) then how we can create?
By using “extends” keyword and we need to implement all abstract method in child class.
If we are unable to implement all abstract method of abstract class in their child class?
We have to make that child class abstract and create child class of that child class and implement that remaining abstract method in that child class as shown in below figure :–

Encapsulation in Java
Encapsulation it means that collection / wrapping of data (data members, constructor, methods, blocks) into a single entity.
Every JAVA class is called an Encapsulated class ( because Encapsulation it means that collection of data members, constructor, methods, blocks into a single entity and every java class consist of all these things).
The best example of encapsulated class is “Setter/Getter class” .
Encapsulation exposes only part of object which are safe to expose and remaining part of object kept safe.
Encapsulation is supported through access control in java, there are 4 type of access control specifier in java (private, protected,default,public) which supports encapsulation.
For example: TV / Laptop manufacturers exposes only the buttons not all the thousands of electronic components which it is made up of.
Public :- can be accessed anywhere.
Protected :- can be accessed within the package and another package of sub-class.
Default :- can be accessed within the package only.
Private :- can be accessed within the class only.
Protected can be accessed outside the package only by it’s child class (method m2()) or child class reference only (method m3()).
Consider the below example, we have 2 packages, com.ajitation with class A & class B and com.ajit with class C.



